IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
QBRELIS® (lisinopril) Oral Solution, 1 mg/mL
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue QBRELIS as soon as possible (5.1).
- Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus (5.1).
INDICATIONS:
QBRELIS is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor indicated for:
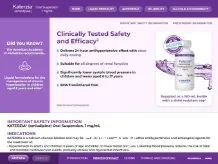
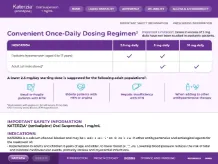
- Treatment of hypertension in adult patients and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older to lower blood pressure (BP). Lowering BP decreases the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions (MI).
- Reduction of signs and symptoms of systolic heart failure.
- Reduction of mortality in treatment of hemodynamically stable patients within 24 hours of acute MI. Patients should receive, as appropriate, the standard recommended treatments such as thrombolytics, aspirin, and beta-blockers.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION:
Contraindications:
QBRELIS is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to lisinopril or any component of QBRELIS, or in patients with a history of hypersensitivity related to previous ACE inhibitor treatment.
QBRELIS is contraindicated in patients with hereditary or idiopathic angioedema.
Do not co-administer aliskiren with Qbrelis in patients with diabetes.
QBRELIS is contraindicated in combination with a neprilysin inhibitor (e.g., sacubitril). Do not administer QBRELIS within 36 hours of switching to or from sacubitril/valsartan.
Warnings and Precautions:
Head and Neck Angioedema: Angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, glottis, and/or larynx, including some fatal reactions, have occurred in patients treated with ACE inhibitors, including QBRELIS, at any time during treatment. Patients with a history of angioedema unrelated to ACE inhibitor therapy may be at increased risk of angioedema while receiving an ACE inhibitor. ACE inhibitors have been associated with a higher rate of angioedema in Black than non-Black patients.
Intestinal angioedema has been reported with ACE inhibitors. Discontinue QBRELIS and obtain appropriate therapy.
Anaphylactoid Reactions: Sudden and potentially life-threatening anaphylactoid reactions have occurred in some patients dialyzed with high-flux membranes treated concomitantly with an ACE inhibitor. In such patients, dialysis must be stopped immediately, and aggressive therapy for anaphylactoid reactions must be initiated. Symptoms have not been relieved by antihistamines in these situations. In these patients, consideration should be given to using a different type of dialysis membrane or a different class of antihypertensive agent. Anaphylactoid reactions have also been reported in patients undergoing low-density lipoprotein apheresis with dextran sulfate absorption and in patients undergoing desensitizing treatment with hymenoptera venom.
Impaired Renal Function: Monitor renal function in patients treated with QBRELIS. Changes in renal function, including acute renal failure, can be caused by drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Patients whose renal function may depend in part on the activity of the RAS (e.g., patients with renal artery stenosis, chronic kidney disease, severe congestive heart failure, post-MI or volume depletion) may be at particular risk of developing acute renal failure on QBRELIS. Consider withholding or discontinuing therapy in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in renal function on QBRELIS.
Hypotension: QBRELIS can cause symptomatic hypotension, sometimes complicated by oliguria, progressive azotemia, acute renal failure, or death. QBRELIS should be started under close medical supervision and followed closely for the first 2 weeks of treatment and whenever the dose of QBRELIS and/or a diuretic is increased. Avoid the use of QBRELIS in hemodynamically unstable patients after acute MI.
Surgery/Anesthesia: In patients undergoing major surgery or during anesthesia with agents that produce hypotension, QBRELIS may block angiotensin II formation secondary to compensatory renin release. If hypotension occurs and it is considered to be due to this mechanism, it can be corrected by volume expansion.
Hyperkalemia: Serum potassium should be monitored in patients receiving QBRELIS. Drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin system can cause hyperkalemia. Risk factors for the development of hyperkalemia include renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, and the concomitant use of potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, and/or potassium-containing salt substitutes.
Hepatic Failure: ACE inhibitors have been associated with a syndrome that starts with cholestatic jaundice and progresses to fulminant hepatic necrosis and sometimes death. If jaundice or marked elevations of hepatic enzymes develop, discontinue the ACE inhibitor and receive appropriate medical treatment.
Adverse Reactions:
See Full Prescribing Information for additional Adverse Reactions (6).
Common adverse reactions where rate on lisinopril exceeds the rate on placebo by at least 2% by use are:
- Hypertension: headache, dizziness, and cough.
- Systolic heart failure: hypotension and chest pain.
- Acute MI: hypotension and renal dysfunction.
Drug Interactions:
Initiation of QBRELIS in patients on diuretics may result in excessive reduction of blood pressure. This can be minimized by either decreasing or discontinuing the diuretic or increasing salt intake prior to initiating QBRELIS treatment.
QBRELIS attenuates potassium loss caused by thiazide-type diuretics. If concomitant use of such agents is indicated, monitor the patient’s serum potassium frequently.
Concomitant administration of QBRELIS and antidiabetic medicines may cause an increased blood-glucose-lowering effect.
In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or with compromised renal function, use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs), including selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors, with ACE inhibitors, including lisinopril, may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. Monitor renal function periodically in patients receiving lisinopril and NSAID therapy.
Dual Inhibition of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): Dual blockade of the RAS with angiotensin receptor blockers, ACE inhibitors, or aliskiren is associated with increased risks of hypotension, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function (including acute renal failure), compared to monotherapy. Closely monitor BP, renal function and electrolytes in patients receiving QBRELIS and agents that effect the RAS.
Avoid use of aliskiren with QBRELIS in patients with renal impairment.
Lithium toxicity has been reported in patients receiving lithium concomitantly with drugs that cause elimination of sodium, including ACE inhibitors. It is usually reversible upon discontinuation of lithium and the ACE inhibitor. Monitor serum lithium levels during concurrent use.
Nitritoid reactions have been reported rarely in patients with injectable gold (sodium aurothiomalate) and concomitant lisinopril therapy.
mTOR or neprilysin inhibitors: Patients receiving coadministration of an ACE inhibitor and a mTOR inhibitor (e.g., temsirolimus, sirolimus, everolimus) or a neprilysin inhibitor (e.g., sacubitril) may be at increased risk for angioedema.
Use in Specific Populations:
See Full Prescribing Information for Additional Information (8).
Pregnancy
QBRELIS can cause fetal harm. See Full Prescribing Information for Additional Information (5.1, 8.1).
Lactation
Because of the potential for severe adverse reactions in the breastfed infant, advise women not to breastfeed while taking QBRELIS.
Pediatric Use
QBRELIS is not recommended in children under the age of 6 years or in pediatric patients with glomerular filtration rate < 30 mL/min/1.73m2.
This Important Safety Information does not include all the information needed to use QBRELIS safely and effectively. Visit QBRELIS.com for Full Prescribing Information.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-461-7449 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/MedWatch.
——————
FDA-7.2